Technology - Ceramics
Generally, ceramics shows the inorganic material of non-metallic crystalline (atom having a regularly arranged structure). Metal oxides, nitrides, generally will include a representative example carbides. Various inorganic compounds phosphate and borate salts of the addition to the metals, and is classified into a ceramic material to the crystalline or amorphous carbon material and a glass material.
Pottery from ancient ceramic material, fine ceramics with various functionality in recent years (Advanced ceramics) is industry, has been active in a wide range of areas of medical care and the like.
Composition and binding mode, express characteristic functions depending on the state of the electron orbit, polycrystalline body (sintered body) in the fine structure also affect the functionality.
For example, silicon carbide SiC has become a silicon atom Si and carbon C, which (see table electronegativity) the difference in electronegativity is less strong covalent, mechanical strength and thermal conductivity it is high.
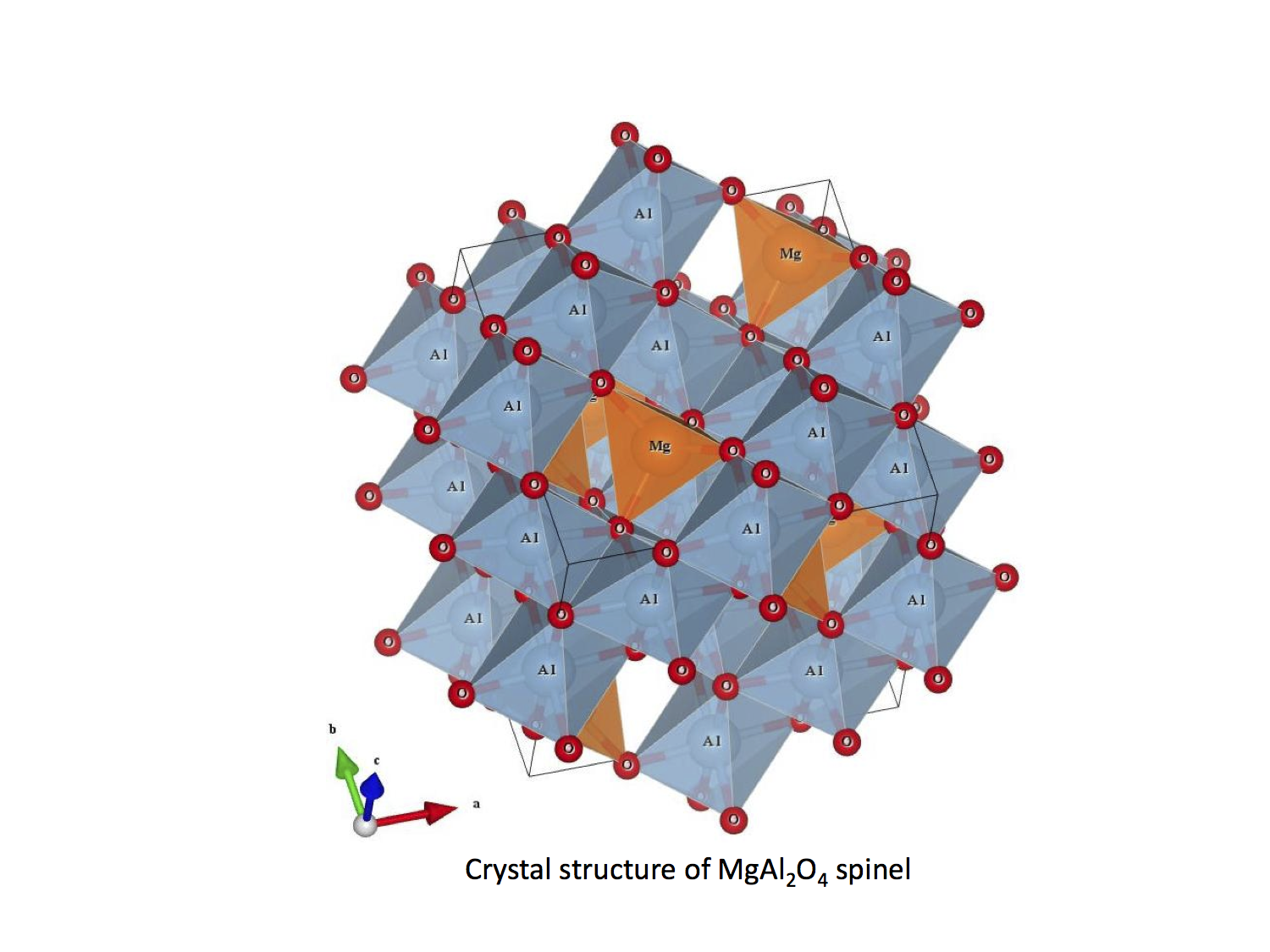
Spinel vs non-Spinel

Electronegativity
Typical Element
| Period | 1 | 2 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | He | |||||||
| 2.2 | - | ||||||||
| 2 | Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | |
| 0.98 | 1.57 | 2.04 | 2.55 | 3.04 | 3.44 | 3.98 | - | ||
| 3 | Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | |
| 0.93 | 1.31 | 1.61 | 1.9 | 2.19 | 2.58 | 3.16 | - | ||
| 4 | K | Ca | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| 0.82 | 1 | 1.6 | 1.81 | 2.01 | 2.18 | 2.55 | 2.96 | - | |
| 5 | Rb | Sr | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| 0.82 | 0.95 | 1.7 | 1.78 | 1.96 | 2.05 | 2.1 | 2.66 | 2.6 | |
| 6 | Cs | Ba | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| 0.79 | 0.89 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 2 | 2.2 | - | |
| 7 | Fr | Ra | |||||||
| 0.7 | 0.9 |
Electronegativity
Transition Metal Element
| Period | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |||||||||
| 2 | |||||||||
| 3 | |||||||||
| 4 | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu |
| 1.3 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 1.9 | |
| 5 | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag |
| 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 1.9 | |
| 6 | La-Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au |
| - | 1.3 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 1.9 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 | 2.4 | |
| 7 | Ac-Lr | ||||||||
First Ionization Energy
Typical Element
| Period | 1 | 2 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | He | |||||||
| 13.598 | 24.587 | ||||||||
| 2 | Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | |
| 5.392 | 9.323 | 8.298 | 11.26 | 14.534 | 13.618 | 17.423 | 21.565 | ||
| 3 | Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | |
| 5.139 | 7.946 | 5.986 | 8.152 | 10.487 | 10.36 | 12.968 | 15.76 | ||
| 4 | K | Ca | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr |
| 4.341 | 6.113 | 9.374 | 5.999 | 7.899 | 9.789 | 9.752 | 11.814 | 14 | |
| 5 | Rb | Sr | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe |
| 4.177 | 5.695 | 8.984 | 5.786 | 7.344 | 8.608 | 9.01 | 10.451 | 12.13 | |
| 6 | Cs | Ba | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn |
| 3.894 | 5.212 | 10.459 | 6.108 | 7.417 | 7.286 | 8.417 | - | 10.749 | |
| 7 | Fr | Ra | |||||||
| 4.073 | 5.278 |
First Ionization Energy
Transitional Metal Element
| Period | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | |||||||||
| 2 | |||||||||
| 3 | |||||||||
| 4 | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu |
| 6.553 | 6.857 | 6.727 | 6.77 | 7.421 | 7.899 | 7.855 | 7.638 | 7.725 | |
| 5 | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag |
| 6.597 | 6.944 | 6.77 | 7.204 | 7.465 | 7.508 | 7.725 | 8.333 | 7.552 | |
| 6 | La-Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au |
| - | 5.512 | 6.076 | 7.986 | 7.855 | 8.723 | 9.201 | 9.027 | 9.201 | |
| 7 | Ac-Lr | ||||||||

